一、红黑树简介
红黑树的规则有
1.每个节点不是红色就是黑色
2.根节点是黑色
3.如果一个节点是红色,它的两个孩子节点是黑色
4.每条路径都有相同数量的黑色节点
5.叶子节点(Nullptr节点)是黑的
这些规则可以推导出红黑树的特性
其最长路径不超过最短路径的两倍,近似平衡
没有连续的红节点
左右子树的黑节点个数相同
其相较于AVL树并没有过多的旋转
用较不平衡换取了性能
在实际中,红黑树的应用相较于AVL树更加常用
二、红黑树的模拟实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
| #pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
enum Color
{
Red,
Black
};
template<class K, class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode* _left;
RBTreeNode* _right;
RBTreeNode* _parent;
Color _col;
pair<K, V> _kv;
RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _col(Red)
, _kv(kv)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = Black;
return true;
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(kv);
if (cur->_kv.first > parent->_kv.first)
parent->_right = cur;
else
parent->_left = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
while (parent && parent->_col == Red)
{
Node* grandpa = parent->_parent;
if (grandpa->_left == parent)
{
Node* uncle = grandpa->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = Black;
grandpa->_col = Red;
cur = grandpa;
grandpa = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(parent);
swap(parent, cur);
}
RotateR(grandpa);
parent->_col = Black;
grandpa->_col = Red;
}
break;
}
else
{
Node* uncle = grandpa->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = Black;
grandpa->_col = Red;
cur = grandpa;
grandpa = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(parent);
swap(parent, cur);
}
RotateL(grandpa);
grandpa->_col = Red;
parent->_col = Black;
}
break;
}
}
_root->_col = Black;
return true;
}
void Print()
{
_Print(_root);
}
bool Inspect()
{
return _Inspect(_root);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
void _Print(Node*& cur)
{
if (cur == nullptr)
return;
_Print(cur->_left);
cout << cur->_kv.first << " ";
_Print(cur->_right);
}
void RotateL(Node*& parent)
{
Node* pparent = parent->_parent;
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
if (pparent == nullptr)
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (pparent->_left == parent)
pparent->_left = subR;
else
pparent->_right = subR;
subR->_parent = pparent;
}
parent->_parent = subR;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL != nullptr)
subRL->_parent = parent;
}
void RotateR(Node*& parent)
{
Node* pparent = parent->_parent;
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
if (pparent == nullptr)
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (pparent->_left == parent)
pparent->_left = subL;
else
pparent->_right = subL;
subL->_parent = pparent;
}
parent->_parent = subL;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR != nullptr)
subLR->_parent = parent;
}
bool check(Node* root, size_t& reference, size_t num)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
if (num != reference)
{
cout << "路径长度有问题" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
if (root->_col == Red && root->_parent && root->_parent->_col == Red)
{
cout << "节点连续红色" << endl;
return false;
}
if (root->_col == Black)
num++;
return check(root->_left, reference, num) && check(root->_right, reference, num);
}
bool _Inspect(Node* root)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
return true;
if (_root->_col != Black)
{
cout << "根节点是红色的" << endl;
return false;
}
size_t leftNum = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == Black)
leftNum++;
cur = cur->_left;
}
return check(_root, leftNum, 0);
}
};
|
三、双红色问题解决原理图
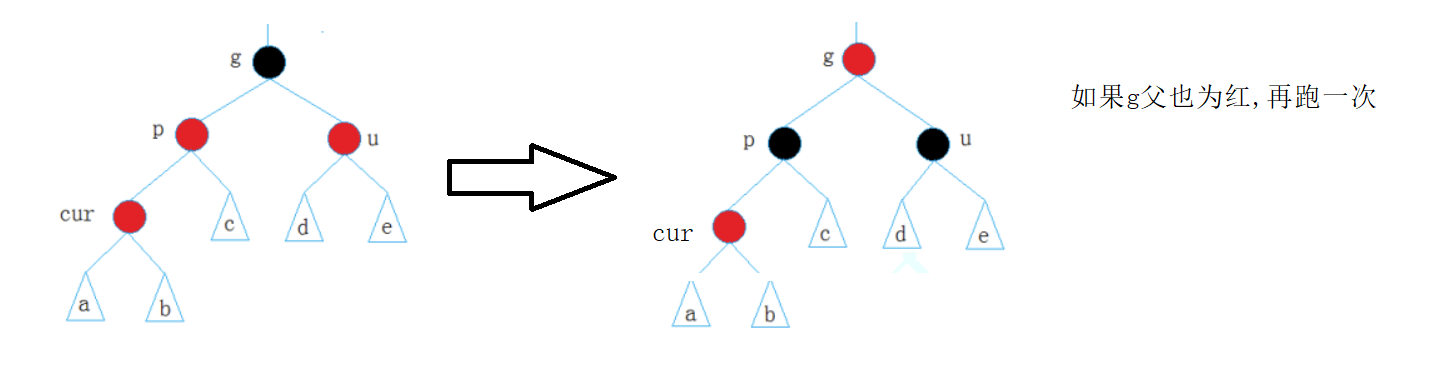
1.叔父同色
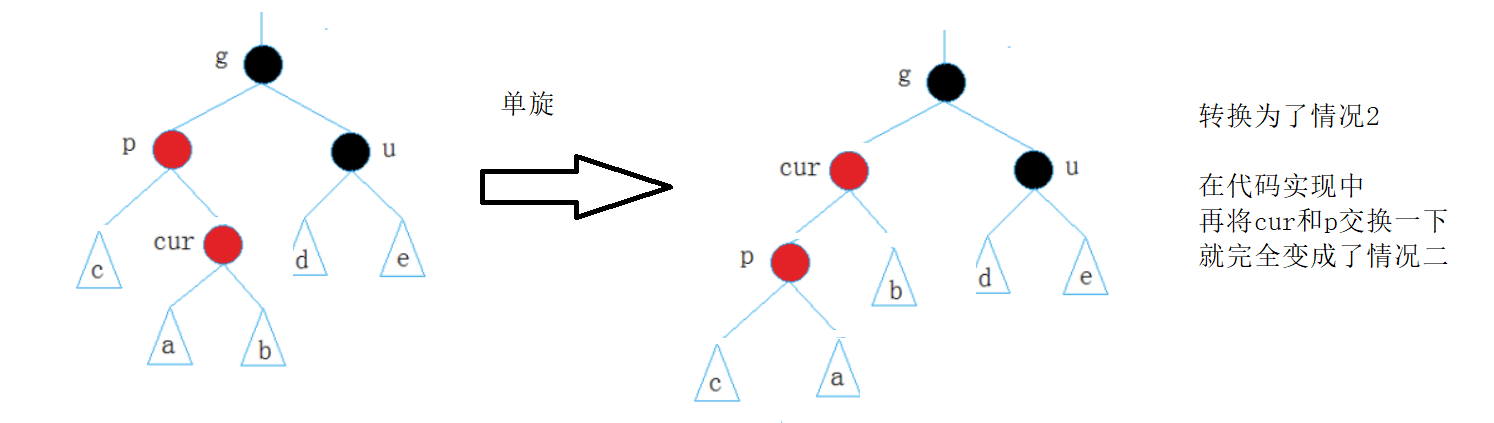
2.叔不存在或为黑,单旋
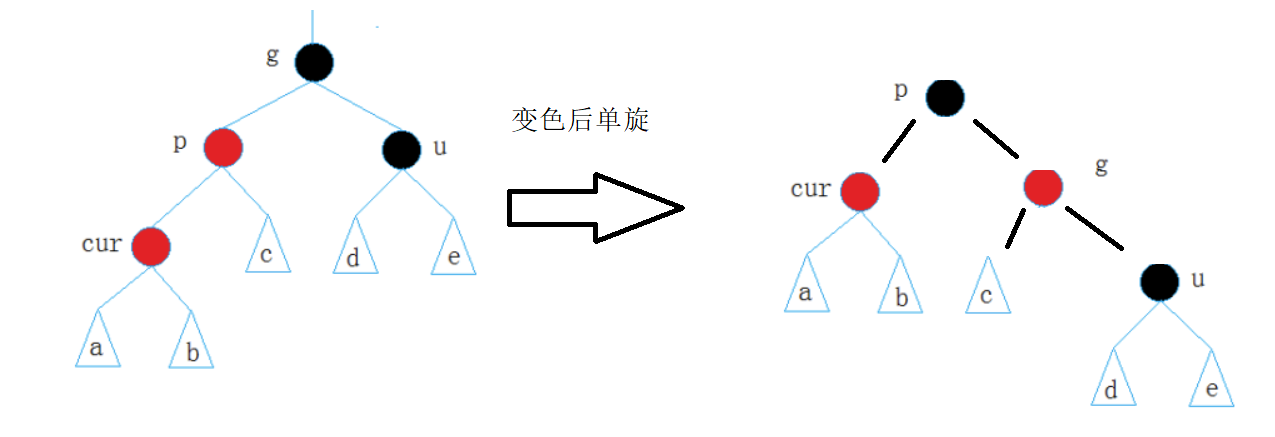
3.叔不存在或为黑,双旋